1. Chance meeting

This is Nine’s Dom Lorrimer’s pic of Tanya Plibersek’s chance meeting with Craig Kelly in the corridors of Parliament House. Continue reading Weekly salon 8/2

This is Nine’s Dom Lorrimer’s pic of Tanya Plibersek’s chance meeting with Craig Kelly in the corridors of Parliament House. Continue reading Weekly salon 8/2
Joe Romm’s article was also posted at RenewEconomy.
We plant about 9 billion trees each year. Unfortunately we also clear about 15 billion, leaving a deficit of 6 billion.
A system of using drones is being developed which could plant trees at 10 times the rate of hand planting and at 20 per cent of the cost by firing germinated seeds into the ground. Continue reading Climate clippings 211
Bloomberg is warning that the multi-trillion-dollar ‘big crash’ in oil investments could start as soon as 2023. However, the smart money is bound to move earlier. Here’s the progress of electric car sales:
The orders came from across the globe even though the car isn’t scheduled for sale until late in 2017.
 Tesla and GM say “they will soon deliver 200+ mile range EVs at a game-changing price of $30,000 or less — including tax incentives.”
Tesla and GM say “they will soon deliver 200+ mile range EVs at a game-changing price of $30,000 or less — including tax incentives.”
For GM, it will be the Chevy Bolt, and for Tesla, the Model 3. Continue reading Tesla and GM announce affordable, long-range electric cars
Via Gizmag, the Immortus solar sports car is so light and aerodynamic, has such a light footprint on the road and so many built-in solar panels, that it is designed to drive for an unlimited range on a sunny day. Continue reading At last, a truly practical solar sports car!
1. Will Hillary Clinton be too weak on climate change?

Campaign chair John Podesta tweeted:
Helping working families succeed, building small businesses, tackling climate change & clean energy. Top of the agenda.
Yet she herself has mentioned it only obliquely since announcing that she’s running. From the past we have this:
At the National Clean Energy Summit in September of last year, in her first major domestic policy address since stepping down from the state department, Clinton described global warming as “the most consequential, urgent, sweeping collection of challenges we face as a nation and a world”. Continue reading Climate clippings 136
1. Accelerating ice loss from Antarctica shelves
Some ice shelves in Antarctica are thickening and some are thinning. The pattern between east and west is obvious from this image:
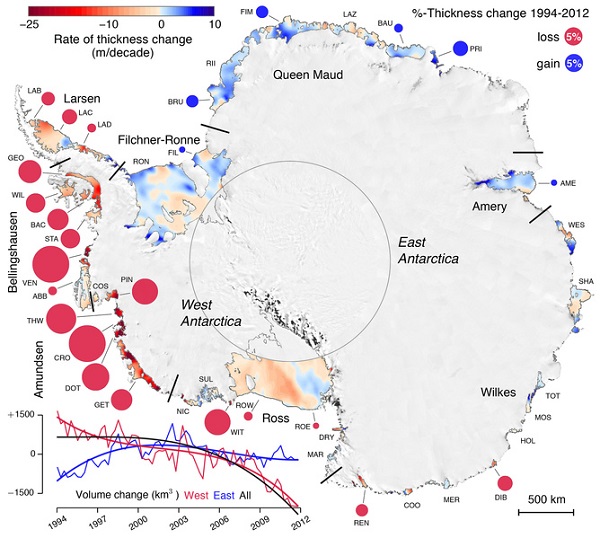
When we sum up losses around Antarctica, we find that the change in volume of all the ice shelves was almost zero in the first decade of our record (1994-2003) but, on average, over 300 cubic kilometers per year were lost between 2003 and 2012.
According to the ABC story, some shelves lost almost 20% of their thickness.
Melting ice shelves does not itself cause sea level rise, but the shelves buttress land ice, which then becomes more mobile. The graph in the bottom corner of the image shows that East Antarctica is now also experiencing a net loss of ice from ice shelves.
2. Top polluters to set own limits virtually penalty free
ANU economist Frank Jotzo said the system is designed so no-one gets caught by it – a toothless tiger. Tony Wood of the Grattan Institute said the ideas proposed in the paper simply would not work. They were commenting on a Government consultation paper outlining “safeguards” to ensure the big polluters do not offset emissions saved through the Emission Reduction Fund (ERF), a flagship component of Direct Action.
Australia’s 140 top polluters will set their own limits for future pollution virtually penalty free, according to the Government’s latest Direct Action policy paper.
Companies subject to the safeguards will select a baseline, or limit, for future pollution.
That baseline will be set according to the highest peak of emissions from the past five years.
Just plain stoopid!
3. What’s going on in the North Atlantic?
Stefan Rahmstorf asks the question at RealClimate. There is a large patch in the North Atlantic which has cooled in the last century.
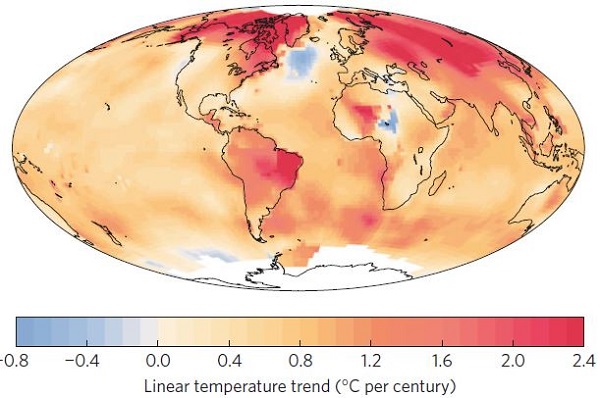
Rahmstorf explains:
Our recent study (Rahmstorf et al. 2015) attributes this to a weakening of the Gulf Stream System, which is apparently unique in the last thousand years.
In fact during last winter, which was the warmest on record for the planet overall, this patch had the coldest temperatures on record.
Chief suspect has to be the increasing freshwater coming off Greenland. There will be consequences.
The consequences of a large reduction in ocean overturning would look nothing like the Hollywood film The Day After Tomorrow. But they would not be harmless either – e.g. for sea level (Levermann et al. 2005) particularly along the US east coast (Yin et al. 2009), marine ecosystems, fisheries and possibly even storminess in Europe (Woollings et al. 2012).
A complete breakdown of the current was given up to a 10% chance this century in the IPCC report. This may have been an underestimate.
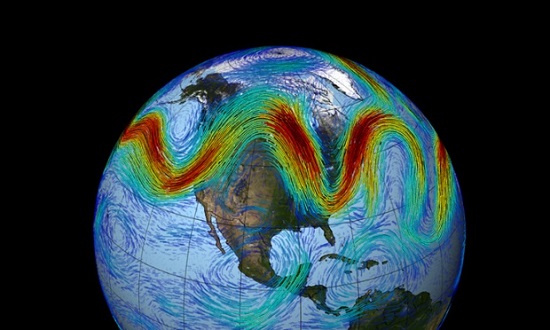
4. Rapid Arctic warming is changing the Jetstream and the weather
Another study, also involving Rahmstorf, looks at changing atmospheric circulation patterns due to Arctic warming.
The Arctic is warming faster than lower latitudes. The Jetstream velocity depends on temperature difference, hence it is slowing. It is also more wavy and has a tendency to get stuck, so heat or cold persists over a large area. Ironically, there is less storminess. Storms transport water onto land and break up persistent weather patterns.
The jet stream that circles Earth’s north pole travels west to east. But when the jet stream interacts with a Rossby wave, as shown here, the winds can wander far north and south.
5. Brisbane EV charging technology takes on the world
Brisbane-based electric vehicle infrastructure company, Tritium, has done a deal to supply its award-winning Veefil DC fast charging stations to America’s ChargePoint company. ChargePoint has 21,000 EV chargers around the US.
The Australian-made stations will be installed on major routes across the country, including the express charging corridors on both the east and west coasts of the US that are being built as part of a recent deal between ChargePoint, Volkswagen and BMW.
The 50kW Veefil stations – which in the US will be called DC Fast stations and will be ChargePoint branded – are able to deliver up to 80 miles or 128 kilometers of charge in just 20 minutes, thus removing one of the key barriers to EV uptake: range anxiety.
Around 16 years ago Toyota unveiled its hybrid electric-gasoline car. Since then it has sold almost six million of them. Now the company is taking a different direction and will start selling cars powered with a hydrogen fuel cell as soon as 2015. The battery car, they say, could only exist as “a niche toy for [rich] eco-snobs”, but is not suitable for the masses.
The fuel cell car will have a range of over 500 km or perhaps as much as 650 km in range driving, and will be refillable in seconds if you can find a filling station. Germany currently has 15.
The price is given as between five and 10 million yen, or about €37,000 to €74,000. Not cheap, but perhaps cheaper than expected as an initial offering.
On the downside, the car is only 30% efficient compared to 70% for battery electric. Hence masses of renewable energy will be required if the cars are to be environmentally friendly. There is a question as to whether sufficient renewable energy will be available for a mass rollout, but the car is more efficient than a conventional petrol model.
Toyota have devoted 500 engineers to the project, so they are certainly serious. Daimler has been working on the concept for some time and expects to have vehicles on the road in 2017, as does a Ford-Nissan alliance. General Motors, Honda and Hyundai are working together on a fuel cell project, Volkswagen has formed an alliance with Canadian fuel cell producer Ballard so as not to be caught out if the technology takes off. Continue reading Toyota’s fuel cell car
 These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as an open thread. Again I do not want to spend time in comments rehashing whether human activity causes climate change.
These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as an open thread. Again I do not want to spend time in comments rehashing whether human activity causes climate change.
This edition contains items, exclusively, I think, in the broad mitigation category.
Estonia with around 1.3 million people achieved the first Nationwide EV fast charging network. Now the Netherlands with about 16.8 million souls has established a contract to build the world’s largest. No citizen will be more than 50 km away from a charging station.
That’s impressive, but given the range of EVs still fairly thin on the ground. Will the charges include the cost of the capital required to roll out the plan? Also if they are going to be “user friendly”, will they sell you coffee while you wait the 15-30 minutes it takes to charge the batteries? Continue reading Climate clippings 81
 This week I’ve concentrated on the practical side of Climate change – mitigation and adaptation and the relevant policies.
This week I’ve concentrated on the practical side of Climate change – mitigation and adaptation and the relevant policies.
According to Giles Parkinson news reports from China indicate that the powerful National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) has proposed a cap on emissions from 2016, from RenewEconomy, picked up at Clean Technica.
What’s more it looks as though China will cease to be an importer of coal within a few years (please note Gina, Clive et al).
Please note also, Tony Abbott and Greg Hunt. The coalition will be phasing out the carbon price just as China is phasing it in. The LNP reckoned a price on carbon was unnecessary because the rest of the world was not going there, remember?
[Update: indigo @ 8 advises that this story is based on a passing comment from a delegate of the NDRC and that no proposal has yet gone forward.]
Two weeks ago Giles Parkinson attended a day hosted by the Carbon Market Institute looking at the future of carbon markets in Australia. It seems that the audience of bankers and such had never taken the Direct Action thing seriously, they thought was just a bit of politicking. Now they are having to face the fact that Greg Hunt, former champion debater, will almost certainly be tasked to implement whatever it turns out to be.
Antony Green’s session was the best attended. The only serious question to be resolved on September 15 is whether the LNP can get the numbers in the Senate. The final numbers, Green explained, can be a lottery, with the balance of power possibly finally held by fringe candidates no-one has heard of. Still markets have to deal with the possibilities and this is how they sit:
The forward curve of the carbon market – such as it is – is pricing odds of 60 per cent that the carbon price will no longer exist by July next year, analysts say. The market odds for it to be gone by 2016 are 80 per cent.
The forward curve for contracts in the National Electricity Market is pricing the odds around the same level. Even Bloomberg New Energy Finance, which said earlier this year that there was just a 30 per cent chance of repeal, is now reviewing that assessment and is likely to lift the odds to above 50 per cent.
And yes, there is an issue of compensation, which doesn’t figure so far in LNP budgeting.
I was intrigued to find a blogger from Knoxville, Tennessee listing five policy briefs released by Australia’s National Climate Change Adaptation Research Facility (NCCARF), with seven more to come by June 30 this year. On closer investigation, I found this speech by Yvette D’Ath officially launching their research portfolio, a portfolio of more than 140 peer-reviewed research projects across 33 universities around Australia. D’Ath praised the work of the scientists and appealed to them for help in countering climate denialism.
Ironic really as the NCCARF is to be wound up by the end of June as there was no more money coming from the Government. More than 100 researchers will be affected nationally.
Instead NCCARF2 will be funded at $3 million per annum for two years as a dissemination project.
The same Knoxville blogger notes the release of the EU Strategy on Climate Change Adaptation which was produced by the Directorate-General for Climate Action, which is a program, not a project, of the European Commission. Their 2013 program of work is worth €20.75 million and the employ 160 people internally and externally.
European technology giant ABB has developed a new technology that will help power the world’s first high-capacity flash charging electric bus system, where buses will receive top up charges in 15 seconds at selected bus stops. A pilot project termed TOSA (Trolleybus Optimisation Système Alimentation) is planned in conjunction with Geneva’s public transport company.
An arm connects with an electricity outlet in the roof of the bus shelter. At the end of the run three to four minutes gives a complete charge. It’s like a trolley bus without overhead wires.
I’m wondering how electric vehicles go with heart pacemakers. I’ve just learned that you can’t use electric hand tools with a pacemaker.
This link has a video showing roughly how the bus shelter connection is made.
It was thought that ‘black carbon’ created by the burning of organic matter such as grass or forests stayed in the soil for millions of years.
By examining carbon in rivers it is now thought that up to 40% of such black carbon dissolves and flows into the oceans.
I gather that soil carbon farming is a different issue, but seems similarly fraught. Di Martin investigated the soil carbon conundrum.
The shorter story is that some exceptional farmers have demonstrated that soil carbon can be increased dramatically. One farmer did this by ‘pasture cropping’. Native grasses were encouraged and the crop was sown directly into the pasture, rather than plowing, harrowing etc.
Another used ‘cell grazing’, which involves high intensity and high rotation grazing, with long rest periods for pasture.
There are problems in measurement, which may be resolvable with new technology. What is not resolvable, however, is the 100-year guarantee required by international protocols if the activity is deemed to benefit the planet.
Bernard Keane, following Lenore Taylor, was rather scathing about Direct Action soil magic.
The fossil fuel incumbents are rolling out a campaign to damage the solar industry. One nasty trick being considered in Queensland is the following:
Gross metering – a proposal made in Queensland which would force households to sell all the output from their rooftop systems to the grid operators, and buy it back at a higher price
Campbell Newman keeps saying that feed-in tariffs PV solar are “just ridiculous”.
The campaign seems to be extending to the whole Coalition policy on renewables, if there is one.
There is increasing concern in the [renewables] industry that the Opposition will pave way for the Renewable Energy Target to be diluted, under pressure from state governments, utilities and generators worried about sliding profits from their coal and gas generators, and noisy anti-renewable lobbies promoted by the likes of [Alan] Jones.
Please note the note at the end of the piece:
it seems the biggest problem the [coal] industry faces is a lack of demand. We’ve noted this before, but this week, this was reinforced by reports from China that imported coal is sitting unwanted and clogging up the country’s biggest ports.
Deutsche Bank energy analysts said this was due to “weak coal demand all over China” which had been apparent since late last year. Indeed, half the coal companies in one region of Mongolia had ceased production of thermal coal because of falling prices, and most small coal mines in Shanxi Province had also closed, Deutsche Bank reported.
Now for something lighter: solar panel art.
