1. Court challenge will test coal mining’s climate culpability
A new legal challenge to the proposed Carmichael coal mine – Australia’s largest – will test in the federal court whether climate change caused by greenhouse gas emissions should be taken into account when assessing prospective coal licences in Australia.
The challenge, by the New South Wales Environmental Defenders Office on behalf of the Mackay Conservation Group, will argue that federal environment minister Greg Hunt failed to take into account the climate impact of greenhouse gases emitted by the burning of coal from the Carmichael mine when assessing whether to grant its licence.
It cites the impact of global warming on the Great Barrier reef, an area of world and national heritage, as a relevant consideration which the minister should have been taken into account.
The linked article cites some of the legal precedents, which show that this case is far from vexatious or frivolous.
Interesting!
2. Queensland Labor renews support for coal

Outgoing deputy Labor leader, Tim Mulherin, said coal remained “an important and vital energy source for Queensland and the rest of the world”.
Thermal coal from nine proposed projects in the Galilee, when burned in export markets such as China and India, would produce an estimated 705m tonnes of CO2, more than Australia’s total greenhouse gas emissions of 542m tonnes a year.
However, Labor in not going to spend hundreds of millions of dollars on building the railway line to the coast.
3. Humanity is in the existential danger zone
Back in 2009 a team lead by Johan Rockstrom of the Stockholm Resilience Centre identified nine planetary boundaries we should not cross if we are to avoid undermining the biophysical systems upon which our species depends. These nine boundaries are climate change, ocean acidification, stratospheric ozone depletion, alteration of nitrogen and phosphorus cycling, freshwater consumption, land use change, biodiversity loss, aerosol and chemical pollution.
A new paper led by Will Steffen of the ANU and the Stockholm Resilience Centre argues that climate change along with “biodiversity integrity” should be recognised as core elements of the Earth system. We are in trouble with both.
The world as we know it developed during the Holocene from which we are rapidly departing. We need urgently to get atmospheric concentrations of CO2 back to 350 ppm.
Background extinction rates without human impacts are thought to be about ten a year per million species.
Current extinction rates are anywhere between 100 to 1000 times higher than that.
4. Catholics in Australia join global movement to curb climate change
Australia’s Catholics are preparing to step up campaigns to address climate change ahead of an expected call to action by Pope Francis.
The Global Catholic Climate Movement, an international coalition of Catholic groups including Catholic Earthcare Australia, was launched on Thursday to bolster support for a global climate treaty at the Paris summit planned for December.
5. NOAA declares 2014 the hottest
NOAA has declared 2014 the hottest year to date with this graphic:
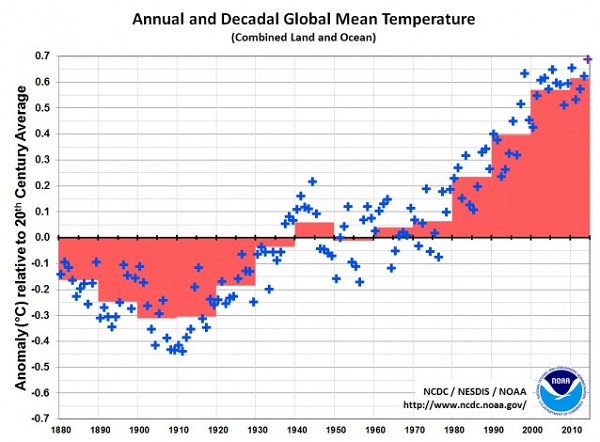
If you drew parallel trend lines from about 1970 it would be full bore ahead with 1998 a slight outlier.
At Climate Central we are told that 13 of hottest 15 years on record have all occurred since 2000. The odds of that happening randomly without the boost of global warming are 1 in 27 million.
6. Sea level rise
There’s been some excitement about a new study of sea level rise. The difficulty in establishing long term trends is that prior to the satellite era (1979, I think) it has been very difficult to establish what happened. Data is globally patchy and incomplete. Tide gauge measurements suffer because the wind blows the water around, and the land that it is referenced to might be rising or sinking.
The clearest account of the new research by Carling Hay and others I’ve found is at Carbon Brief. Hay et al found sea levels from 1900 to 1990 to be 1.2 mm pa on average, lower than the 1.5 previously thought. This makes current sea level rise some two and a half times faster, with the implication that ice sheets a contributing more than previously thought.
Over at RealClimate Stefan Rahmstorf gives a technical review of the state of play. He regards the new research as important, but his bottom line is this:
Ultimately, it is not clear down to what level of accuracy we will ever know the sea level evolution over the past hundred years or so. But for practical purposes, I don’t think it matters whether the rise from 1900 AD has been 3 centimetres more or less. I do not think this changes our outlook for future sea-level rise in any significant way.
But if I understand him correctly, he would already have been considerably concerned about the decay of ice sheets and how that process could accelerate. However, he strikes me as wanting to be super careful not to run ahead of the data, which is entirely commendable.
One comment was that this research could add a metre to prospective sea level rise this century. I think Rahmstorf is suggesting that is premature.

