This edition contains a miscellany from the absolutely central scientific issue of climate sensitivity to adaptation in Bangladesh.
This edition contains a miscellany from the absolutely central scientific issue of climate sensitivity to adaptation in Bangladesh.
1. Sense about climate sensitivity
The fourth IPCC report in 2007 estimated that the planet will warm between 2 and 4.5°C warming in response to a doubling of the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere, with a best estimate of 3°C. Since then a number of studies suggested a lower sensitivity, leading the IPCC’s fifth report to extend the range to 1.5°C at the lower end and omit a best estimate entirely.
Dana Nuccitelli reports on a new paper by Kummer & Dessler which shows that recent studies suggesting an insensitive climate are flawed. Without going into the detail they converge on a value around 3°C.
2. CO2 fertilization won’t slow global warming
Some contend that increased CO2 in the atmosphere will enhance plant growth leading to an increase in soil carbon. A study of this issue found that any such gains were offset by increased microbial activity in soils. Along the way the researchers found that soil carbon was less stable than previously thought.
3. Bangladesh uncovers the crippling cost of climate change adaptation

Bangladesh has found the cost of climate change adaptation quite crippling in a new report.
They are spending $1 billion a year, 6-7% of their annual budget, on climate change adaptation. Only a quarter comes from aid.
The irony of the finding will be lost on few people: the average European citizen emits as much carbon in 11 days as the average Bangladeshi in an entire year. Yet it is the government and the people of Bangladesh who are expected to pay for the escalating costs.
Within the country it is the poor who are most severely affected.
After the report Bangladesh sees climate adaptation expenditure as central to their development.
4. Deutsche Bank rules out funding for controversial Abbot Point coal terminal
said it would not finance an expansion without the assurance of both the Government and UNESCO that it would not damage the Great Barrier Reef.
“We observe that there is no consensus between UNESCO and the Australian Government regarding the expansion of Abbot Point,” it said.
“Since our guidance requires such a consensus as a minimum, we would not consider a financing request.”
Thanks to John Davidson for the heads-up.
5. Onshore wind cheapest form of power
In Europe, that is according to Portugal’s EDP, which has around 24GW of generation, of which around 8.7GW is in onshore wind.
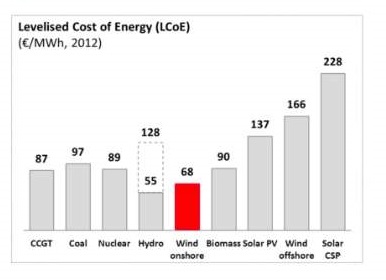
CCGT is baseload gas.
John D has more detail at Climate Action 04.
The same article tells us that Keith DeLacy, former Qld Labor treasurer who would do just about anything to turn a buck, said on the front page of the Oz that renewables had “no place in a modern society”.
Meanwhile economist Jeffrey Sachs, advisor to UN secretary general on the Millennium Development Goals, is in Australia telling us that we can’t mine all that coal unless we invest in carbon capture and sequestration technology. We just need to get serious:
Put in real money, probably $20 to $30 billion I would say, minimum, to get scaled, serious demonstration programs working in China, in India, in Australia, in Canada, in the United States and to test the geology and the engineering of this technology.
Sachs is a man who thinks big!
6. EU’s energy strategy
Not surprisingly, the EU has been taking another look at its energy security strategy in view of the political instability to their east.
The EU imports over half the energy it consumes at a cost of more than €1 billion per day. Two-thirds of its gas is imported, with nearly a third coming from Russia. Half of that is transported via Ukraine.
Russia has already twice pulled the plug on gas supplies to Europe arriving via Ukraine, in 2006 and 2009.
The bottom line is that there will be a continued dependence on Russia for the foreseeable future:
The EU energy security strategy doesn’t look like it’ll take a rifle to that Russian bear just yet. But with a tweak to address vulnerability here and a spotlight on energy dependence there it may just help the EU avoid a mauling – and drive an ambitious EU 2030 climate and energy deal too.
Shale gas and nuclear energy are being left as options that member states can explore if they wish.
Reminder: Use this thread as an open thread on climate change.