1. Ocean acidification charted
Apparently there has been no baseline data for ocean acidification, which varies around the world. Now a database of the current state of the ocean has been compiled. Here is a map showing the rough state of play:
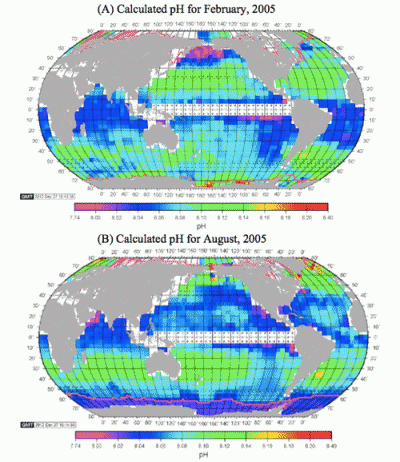
The current rate of acidification for the ocean is the greatest seen in the past 300 million years. 25% of co2 emitted ends up in the ocean.
This article offers some hope that some species may adapt.
2. Warmest October
NASA has October as the warmest since 1880 along with 2005. The Japanese Meteorological Agency has it as the warmest ever:
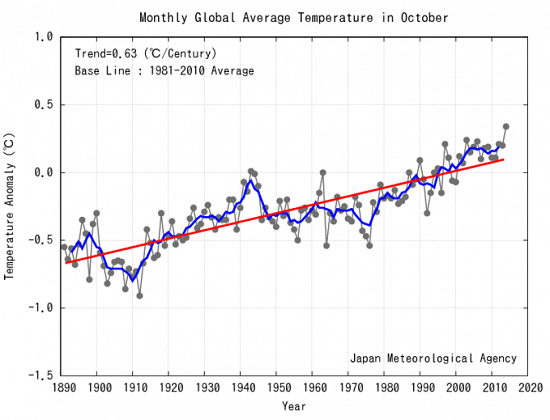
No warming pause there!
So far an El Niño still has not developed, which would make things warmer.
3. Climate Council report fingers us
The Climate Council has published a new report Lagging Behind: Australia and the Global Response to Climate Change. The key findings are:
- China and the US have firmly moved from laggards to global leaders on climate change.
- In the last five years most countries around the world have accelerated action on climate change as the consequences have become more and more clear.
- Australia, a crucial player in global climate action, moves from leader to laggard.
- Global action must accelerate to protect Australia and the world from the consequences of a changing climate, sea level rise and more frequent and intense extreme weather.
Now, 39 countries and over 20 sub-national jurisdictions are putting a price on carbon. China has the world’s second largest carbon market with 250 million people covered. In the US 10 states have carbon markets, covering 79 million people.
Germany has decoupled growth from carbon pollution. Since 1990 GDP has increased 37% while emissions have fallen 25%.
According to the IEA and the OECD for every $1 spent to support renewable energy, another $6 is spent on fossil fuel subsidies, but investment in renewable energy at US$192 billion now exceeds that in fossil fuel energy at US$102 billion.
Australia is the 15th largest emitter out of 186 countries. We emit roughly the same as France, Italy and Turkey, each with three times the population.
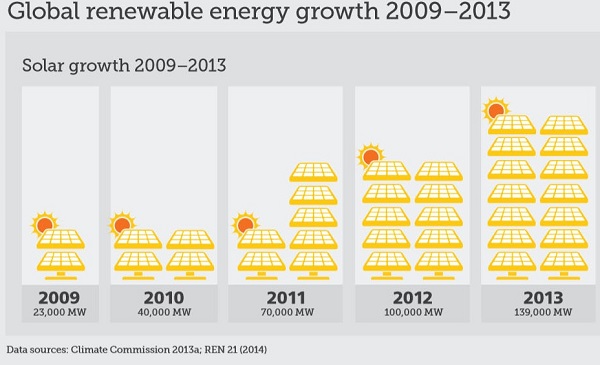
Here’s the world wide solar growth:
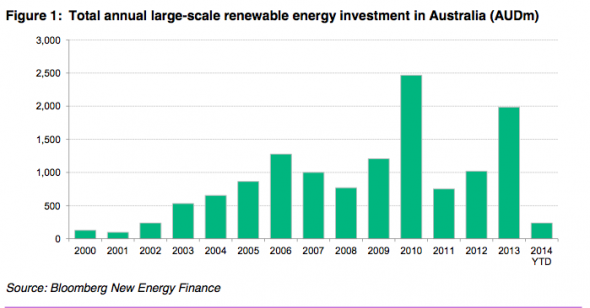
Our record on large scale renewables:
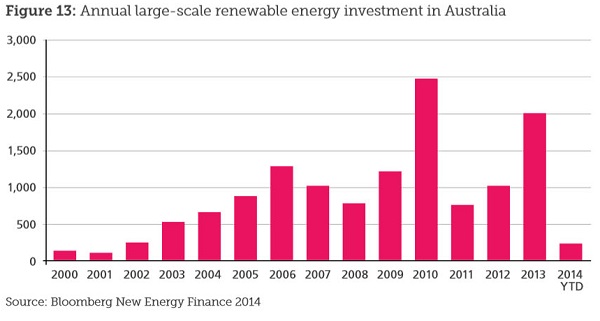
Time to get on our bike!
4. Climate Council on renewables
The Climate Council report finds that around the world important initiatives on renewables are often taken at the sub-national level. In Australia:
- South Australia is striding forward leading the Australian States on renewable energy.
- Victoria and NSW have moved from leaders to laggards in Australia’s renewable energy race.
- Australia has substantial opportunities for renewable energy. A lack of clear federal policy has led to a drop in renewable energy investment.
Only SA and the ACT have renewable energy targets – SA 50% of electricity by 2025, the ACT 90% by 2020. The current state of play is:
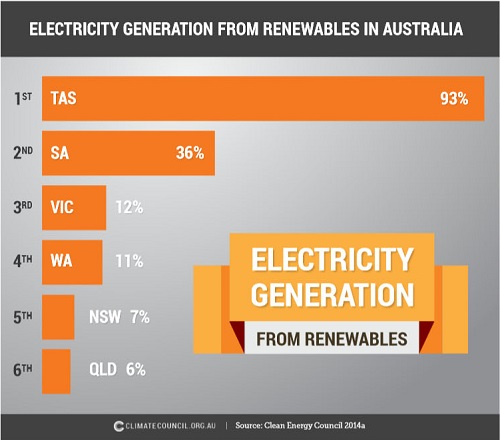
SA narrowly pips QLD in terms of percentage of dwellings with solar PV:
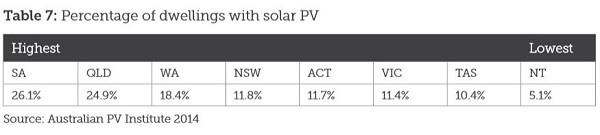
Both have roughly a quarter.
The potential for renewables in Australia is huge – some 500 times current electricity generation.
Australia produces per capita 23.96 tCO2e as against an OECD average of 12.47. As I said, time to get on our bike!
5. China caps coal use by 2020
The Chinese government announced Wednesday it would cap coal use by 2020. The Chinese State Council, or cabinet, said the peak would be 4.2 billion tonnes, a one-sixth increase over current consumption.
This is a staggering reversal of Chinese energy policy, which for two decades has been centered around building a coal plant or more a week. Now they’ll be building the equivalent in carbon-free power every week for decades, while the construction rate of new coal plants decelerates like a crash-test dummy.
The 2020 coal peak utterly refutes the GOP claim that China’s recent climate pledge “requires the Chinese to do nothing at all for 16 years.” Indeed, independent analyses make clear a 2020 coal peak announcement was the inevitable outcome of China’s game-changing climate deal deal with the U.S. last week, where China agreed to peak its total carbon pollution emissions in 2030 — or earlier.
6. Australia a pariah
Giles Parkinson thinks other nations are deliberately trying to embarrass Australia on climate change. Certainly Obama’s remarks can be interpreted that way. Then he (Giles) really gets stuck in:
We are, quite possibly, witnessing the most incompetent and ideologically blind government ever to hold power in Canberra. It’s effectively the Tea Party of Australia, pretending to be something else.






 These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as a roundtable. Again, I do not want to spend time in comments rehashing whether human activity causes climate change.
These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as a roundtable. Again, I do not want to spend time in comments rehashing whether human activity causes climate change.

 These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as an open thread. This post has emphasised adaptation and mitigation, essentially what we need to do to achieve a safe climate.
These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as an open thread. This post has emphasised adaptation and mitigation, essentially what we need to do to achieve a safe climate.
 This week I’ve concentrated on the practical side of Climate change – mitigation and adaptation and the relevant policies.
This week I’ve concentrated on the practical side of Climate change – mitigation and adaptation and the relevant policies.