That image is a shot of the earth rising over the moon, photographed on Christmas Eve 1968 from Apollo 8, taken from a 2016 article by Martin Rees, looking at the dawn of the Anthropocene.
He plots two futures, one where we continue to degrade the planet, another more optimistic, where human societies could navigate current threats, achieve a sustainable future, and inaugurate a future more marvellous than what was achieved in the Holocene. He is interested in humans becoming electronic beings, which I’d see as a dystopia. Nevertheless, if humans act together, in the interest of the the broad ecology, including our species as a whole, our future could be bright.
In the real world we take action within nation states, which typically put the nation’s interest, however derived, ahead of other nations or indeed ahead humanity as a whole.
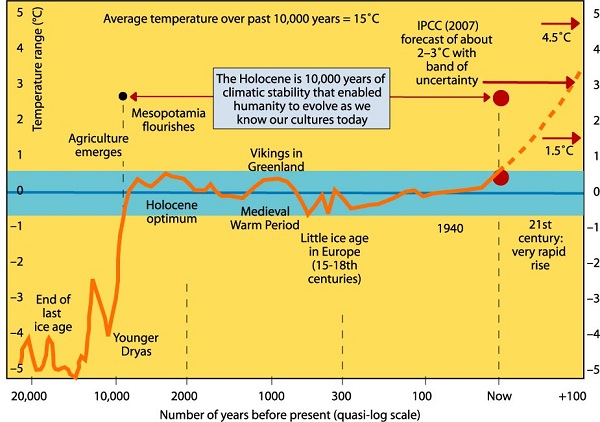
Internationally through the IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) and the UNFCCC (United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change) we are offered scenarios on climate change where, at best, the already bad will get worse. In the case of the latest IPCC 1.5°C report we are offered a 50% chance of avoiding the worst of a dangerous climate. Meanwhile, even if ‘successful’ sea levels will continue to rise, the Great Barrier Reef will be devastated, bad weather, droughts, floods and wildfires will get worse.
Unfortunately in Australia we have a government in power that intends to meet it’s commitments through cheap accounting tricks, where its environment department sees emissions continuing to rise through to 2030. Given that we are one of the largest per capita emitters in the OECD, our Paris commitments are exceptionally modest at 26-28% from 2005 levels. Those were initial commitments. A point overlooked is that under the Paris Agreement parties we undertook to ratchet up our commitments post 2020.
So what should Labor do if elected in 2022 to work towards a safe climate and a world were responsible growth and development is possible? What is a climate emergency, and can we respond appropriately? Continue reading Climate emergency – ecological sustainability within planetary boundaries, and a safe climate →



 ‘Tipping point’ is a metaphor, first used by science and the media about climate change from about 2005
‘Tipping point’ is a metaphor, first used by science and the media about climate change from about 2005