 This is a continuation of the Climate clippings series familiar to readers of Larvatus Prodeo
This is a continuation of the Climate clippings series familiar to readers of Larvatus Prodeo
While this edition was finished about a week ago I actually started writing stuff from about mid-February and have several others queued in the draft bin. They’ll be fed in periodically at the rate of perhaps more than one a week until I catch up with myself.
1. Strong El Niño rated an 80% chance
That’s according to Paul E. Roundy of the University at Albany, New York.
The sub surface temperature of the eastern Pacific Ocean is measuring an ‘astounding’ six degrees warmer than normal for this time of year.
The only time anything similar has happened was in March 1997, before the whopping 1998 El Niño.
An El Niño normally means dry conditions and reduced monsoons in Australia and Indonesia, but wetter weather in Central America.
Climate Progress shows this interesting graph:
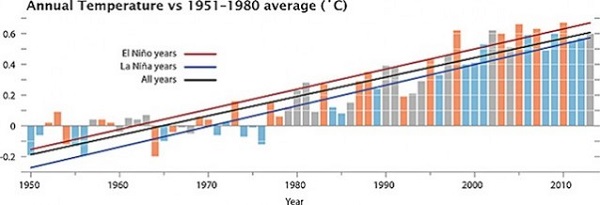
Since 1998 there have been six La Niña years warmer than any El Niño years prior to 1998.
At Mashable Andrew Freedman quotes the same people but found at least one scientist who thinks there’s perhaps a 40% chance there will be no El Niño at all.
Worth watching. Could be spectacular.
Climate Progress reports on wave energy projects at Morro Bay in California and elsewhere.
A 2012 report prepared by RE Vision Consulting for the Department of Energy found that the theoretical ocean wave energy resource potential in the U.S. is more than 50 percent of the annual domestic demand of the entire country. The World Energy Council has estimated that approximately 2 terawatts — 2 million megawatts or double current world electricity production — could be produced from the oceans via wave power.
3. The Pacific Ocean is turning sour
Much faster than expected, according to a new study.
Apparently CO2 concentrations are not uniform around the world and the tropical Pacific is getting more than its fair share. Hence the ocean in that area is acidifying faster than elsewhere.
4. Oxfam on food futures
From Huff Post, Oxfam has just completed a report (downloadable here) which suggests that climate change could delay the fight against world hunger for decades. Global food prices could double by 2030, with half the increase attributable to climate change. In the next 35 years there could be 25 million more malnourished children under the age of five than there would otherwise be.
Oxfam analyzed ten gaps that measured how prepared – or unprepared – 40 food-insecure countries are to tackle climate change impacts.
We assess ten key factors that influence a country’s ability to feed its people in a warming world – these include the quality of weather monitoring systems, social safety nets, agricultural research and adaptation finance.
As expected, the poorer countries will be most affected.
5. Will we still be able to have a decent cup of tea?
At the foot of the Huff Post Oxfam link above is a graphic showing the top “endangered” crops listing in order chocolate, coffee, beer (at least in Germany), peanuts, durum wheat to make pasta in Italy, maple syrup, honey, wine (at least in France). It must be said that I couldn’t find that list in the Oxford report which is mainly about staples such as rice and vegetables.
Now it seems that Assam tea is being affected by hotter, drier weather with more erratic rainfall. Indeed tea growing all over the world is becoming more difficult.
There’s more at the BBC.
6. More on global food security
A separate study found that from 2030 onwards, the world’s crop yields will be more and more impacted by climate change.
The study found that Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia showed significant yield reductions for the second half of the century, while regions of the world with temperate climates, such as Europe and most of North America, could withstand a couple of degrees of warming without a noticeable effect on harvests, or possibly even benefit from a bumper crop.
One of the most important findings of this study is that adaptation may not be as effective for rice and maize as it is for wheat.
7. On the other hand
If you need a more cheerful story, here’s one about peasant farmer Vu Thi Ngoc who has adapted to crazy weather in the uplands of northern Vietnam by growing a different range of crops and changing farming practices.
It shows adaptability at work, this time with the help of CARE and Vietnam’s Agriculture and Forestry Research and Development Centre for the Northern Mountainous Region.
Reminder:
These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as an open thread.
But as ever, I do not want to spend time in comments rehashing whether human activity causes climate change.

 These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as a roundtable. Again, I do not want to spend time in comments rehashing whether human activity causes climate change.
These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as a roundtable. Again, I do not want to spend time in comments rehashing whether human activity causes climate change.

 These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as a roundtable. Again I do not want to spend time in comments rehashing whether human activity causes climate change.
These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as a roundtable. Again I do not want to spend time in comments rehashing whether human activity causes climate change. These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as an open thread. This post has emphasised adaptation and mitigation, essentially what we need to do to achieve a safe climate.
These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as an open thread. This post has emphasised adaptation and mitigation, essentially what we need to do to achieve a safe climate.
 This week I’ve concentrated on the practical side of Climate change – mitigation and adaptation and the relevant policies.
This week I’ve concentrated on the practical side of Climate change – mitigation and adaptation and the relevant policies.

