The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has published its Emissions Gap Report 2014 a couple of weeks before the UN Conference on Climate Change in Lima, Peru. The latter is the annual UNFCCC Conference of Parties (COP), the penultimate one before the 2015 conference in Paris where, with a bit of luck, legally binding medium and long-term targets will be set for each country for emissions reduction. Each year since Copenhagen in 2009 the UNEP has reported on the gap between explicit pledges made by member states and what is required to have a likely (67%) chance of the planet staying within the 2°C guardrail. This is a necessary activity, because since Copenhagen each country determines its own targets within a framework of “common but differentiated responsibility”, which is a bunch of words that effectively allow each country to do as it pleases.
Someone needs to keep a tally as to what all this voluntary activity adds up to. UNEP had taken on that role.
The UNEP report takes note of and is broadly consistent with the IPCC Synthesis Report. Hence it accepts the IPCC ‘budget approach’ which states that we have already emitted 1,900 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide (Gt CO2) from an allowable budget of 2900 Gt since the dawn of the industrial era, leaving an estimated remaining budget of just 1,000 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide (Gt CO2). That’s roughly 20 years worth of emissions at the current rate.
Whereas the IPCC has given a range of scenarios, (scientists giving a range of options to policy makers) the UNEP has plotted just one which sees us peaking within about 10 years, halving CO2 emissions by 2050 and reaching net zero thereafter, they say between 2055 and 2070.
Net zero implies that some remaining CO2 emissions could be compensated by the same amount of carbon dioxide uptake, or ‘negative’ emissions, so long as the net input to the atmosphere due to human activity is zero, the report finds.
Because this scenario involves overshoot we will have to have net negative emissions during the last decades of the century. The less we act now the harder it gets later, as illustrated here:
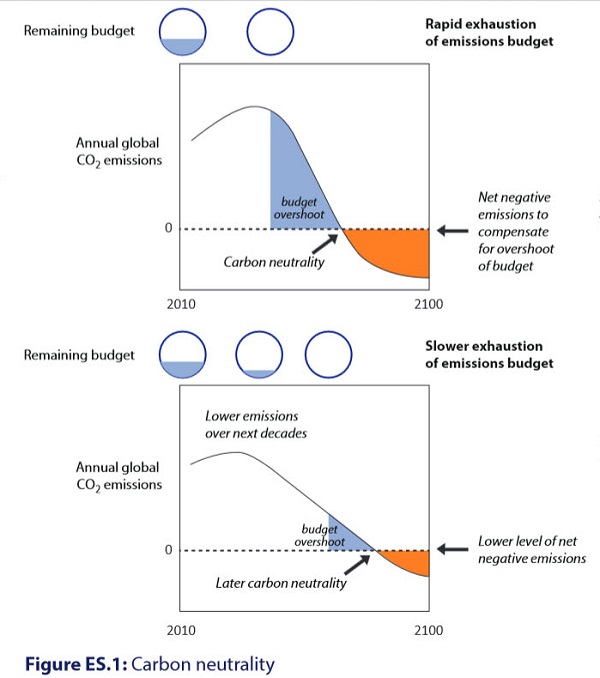
Hopefully this will sink into the brains of those attending the Lima conference, and more importantly the brains of their masters back home.
UNEP have done the sums and find that emissions in 2020 should not be higher than 44Gt CO2e to have a 67% chance of staying within
the 2°C target. If countries honour their current pledges we are heading for 52–54 Gt CO2e in 2020, leaving a gap of 8–10 Gt CO2e.
UNEP then looked at whether countries were on track to honour their pledges.
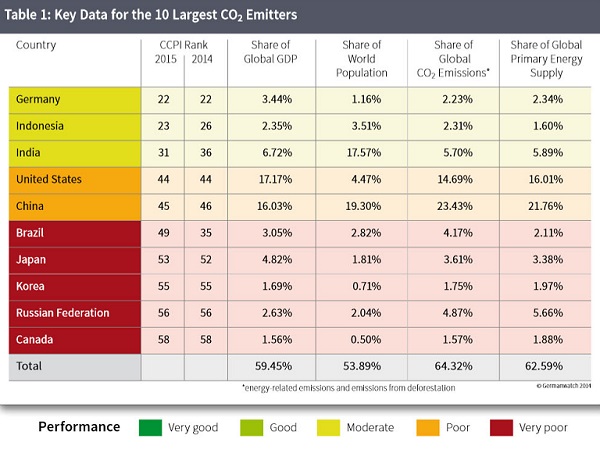
After reviewing available evidence from the G20 (with the EU 28 taken as a group) it appears that five parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change – Brazil, China, the EU28, India and the Russian Federation – are on track to meet their pledges. Four parties – Australia, Canada, Mexico and the USA – are likely to require further action and/or purchased offsets to meet their pledges, according to government and independent estimates of projected national emissions in 2020. Conclusions are not drawn for Japan, the Republic of Korea, Indonesia and South Africa because of various uncertainties, nor for Argentina, Turkey and Saudi Arabia because they have not proposed pledges.
In 2010 we were at 49Gt CO2e; in 2020 we are likely to be at 55 Gt CO2e. The broad situation out to 2030 is represented as follows:
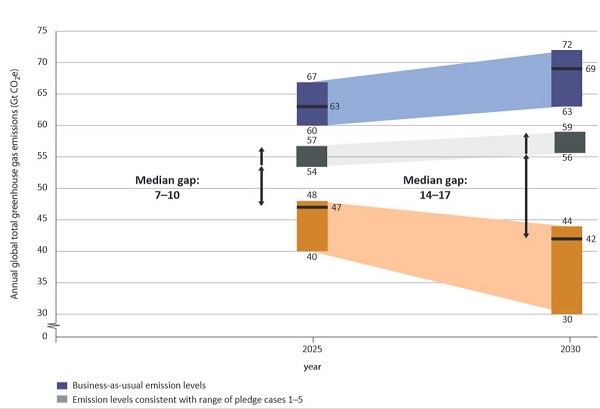
I take it that our current form will get us to 56 to 59 Gt CO2e (grey), whereas we should at the very least be at 42 Gt CO2e (in the orange zone).
The gap is still widening.
There are several comments that need to be made.
First, the UNEP calculations would not have taken on board the China-US agreement. As stated in that post, Climate Interactive worked out that if other countries matched the US-China effort the following stabilisation scenario would ensue:
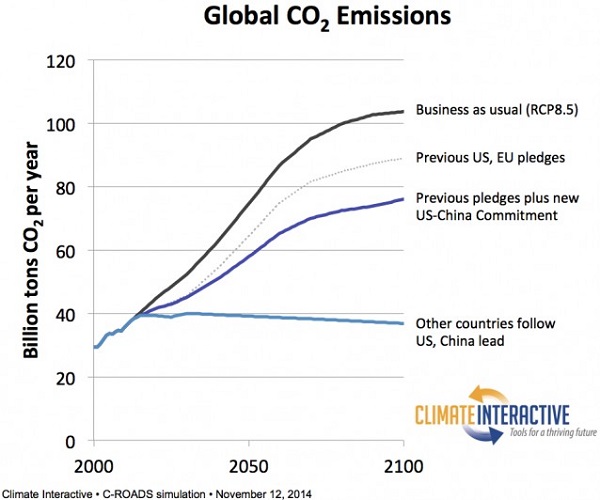
For the first time we have a prospect of peaking emissions, but this does not come within a bulls roar of zero emissions in the second half of this century. The current level of ambition is lamentably lacking.
Secondly, and admirably, the UNEP report takes into account all greenhouse gases from all sources, calculated in terms of CO2 equivalent. Too often scientific reporting is limited to fossil fuel emissions.
Thirdly, the report is conceived within a framework that is irresponsible, bordering insane. A 67% chance of not breaching the 2°C guardrail represents lousy odds when we are dealing with the viability of major ecosystems on the planet and the future of civilisation.
The 2°C guardrail itself is now clearly inappropriate, when, for example as I explained in this post and elsewhere that preserving more than 10% of coral reefs worldwide in 2100 would require limiting warming to below 1.5°C.
The World Bank report Turn down the heat contains examples like this:
In Brazil, at 2°C warming, crop yields could decrease by up to 70 percent for soybean and up to 50 percent for wheat.
The scientists from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and Climate Analytics who put that report together for the World Bank are telling it like it is. Sadly the international array of scientists and others involved in the UNEP report (plenty of Germans but none I can see from Potsdam) are making concessions to what they think will be politically acceptable and doable, as, unfortunately, does the IPCC report.
The stakes are too high for such dissembling diplomacy!
Update: Len @ 1 asked:
It would be nice to at least know what level of action is needed to reach a 95% level surety. Is this stated anywhere?
Back in 2008 James Hansen told us that we had already overshot and that in the first instance we should get concentration levels down to 350 CO2e. Hower, he seems to be about a decade ahead of the bulk of the scientific/political community concerned with climate change. The 2°C guardrail had been invented by the Germans in the 1990s and was accepted by the UNFCCC process as a desirable aim in Copenhagen in 2009. Since then it has become the ‘widely accepted standard’ we should aim at. As such it provides the framework within most climate mitigation scientists work.
The IPCC Fifth Assessment report (AR5) (my post on the Synthesis Report here – see second table) did not look at stabilisation scenarios aiming at less than 450 ppm CO2e. They have a column for <430 but didn't fill it in, because of a lack of studies in the scientific record. The IPCC relies on studies in the scientific literature, with a cutoff of about December 2012, and insufficient studies were available for them to fill in the numbers.
So the failure is with the scientific community, sadly.
I can give you two pointers. The first is this wondrous graph which I first picked up in The Climate Authority Review of targets:
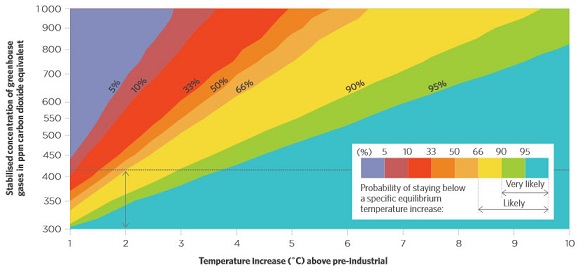
The graph has Malte Meinshausen’s name on it. He was at the time at the Potsdam Institute, I believe he is now at the University of Melbourne. His work is excellent.
From the graph you can see that 350 ppm will only get you about a 95% chance of staying below 2.5°C, not 2°C.
If you want a 1.5°C climate you need about 320 ppm. We are currently at 480 ppm CO2e.
It is notable that David Spratt and Philip Sutton wrote in 2008 that we should be aiming at 320 ppm. Spratt blogs at Climate Code Red, where under Publications you will find a book by the same name which was originally published online in 2008 as The Big Melt written in response to the astonishing Arctic melting in 2007, since easily surpassed in 2012. Spratt is a science writer rather than a scientist, and consistently publishes critiques of the mainstream approach, as I picked up, for example in The game is up, where he says:
We have to come to terms with two key facts: practically speaking, there is no longer a “carbon budget” for burning fossil fuels while still achieving a two-degree Celsius (2°C) future; and the 2°C cap is now known to be dangerously too high.
He concludes that there is no longer a non-radical option, only one path remains viable: the emergency ‘war economy’ mode.
Climate Code Red identifies practical strategies we need to adopt.
The Australian group Beyond Zero Emissions consistently publish material on rapid decarbonistaion. My mate John Davidson has investigated them more than I have and regards them as sound. I hope to post on one of their reports soon.
Elsewhere Kevin Anderson from the UK is worth keeping an eye on. See his personal site and Real clothes for the emperor.
Professor John Wiseman, Deputy Director of the Melbourne Sustainable Society Institute at the University of Melbourne looked at the shape of climate policy for the future for the Centre for Policy Development. See Climate change: reconnecting politics with reality. He has an appropriate sense of urgency and sets out the specific strategies we need to adopt in Australia for rapid decarbonisation. He, for example, sees the need for 100% renewables in 10 years.
People like Spratt, Anderson, Wiseman and BZE are all looking for “the achievement of emission reductions at the necessary scale and speed [which] will require transformational rather than incremental change”. The war analogy is not inappropriate. Abbott would have us fiddle while Rome burns. His approach is essentially one of tokenism. You run a climate mitigation program off to one side in order to have one on your books, at the least expense you can get away with. It’s essentially a sop to the electorate which doesn’t interrupt your central vision of the generation of wealth based centrally on the fossil fuel industry.
This is delusional – see The folly of Galilee basin coal.