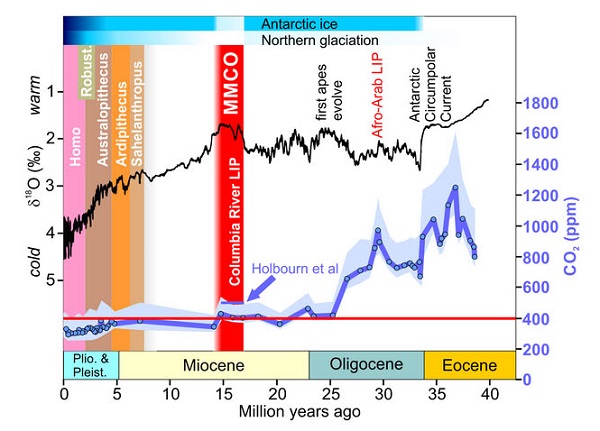
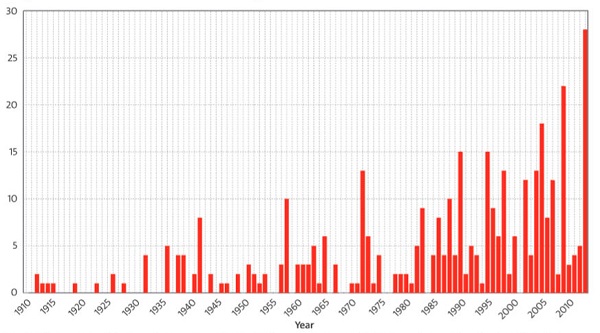
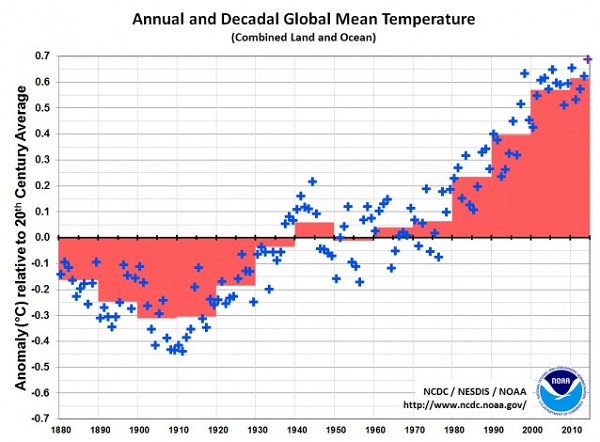
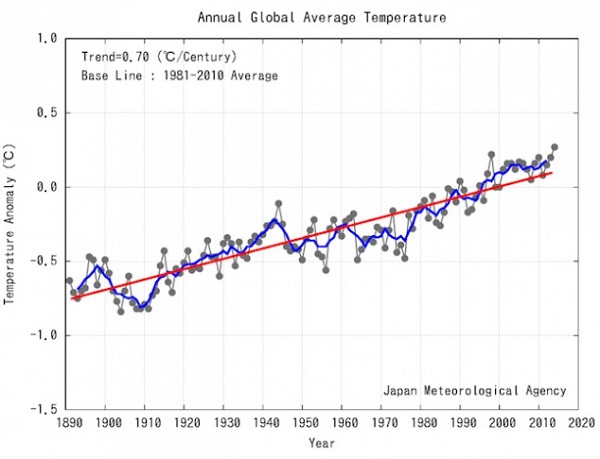
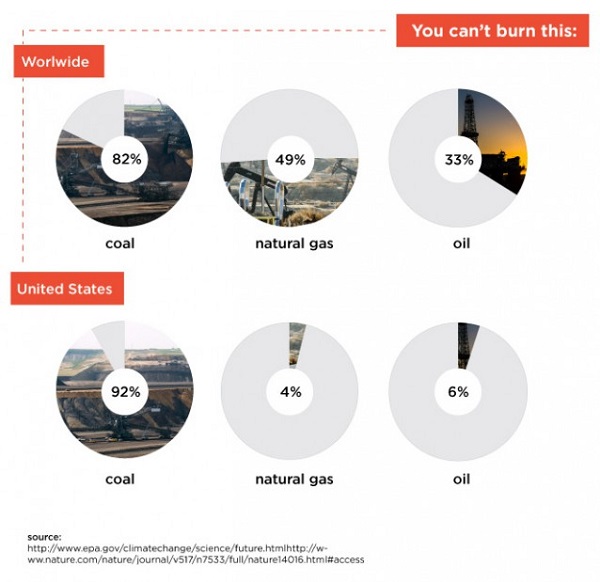
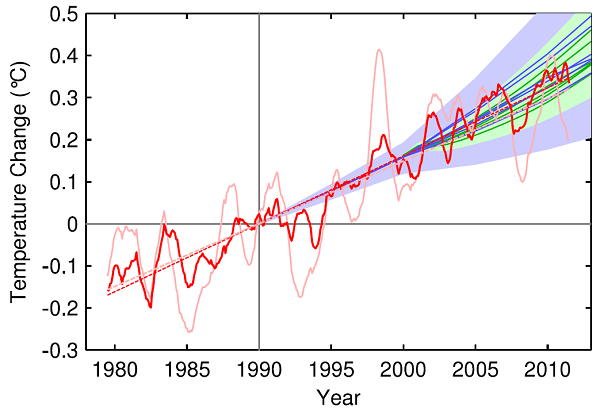
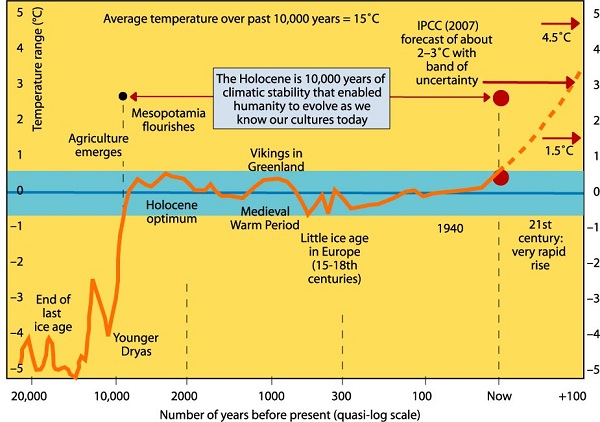
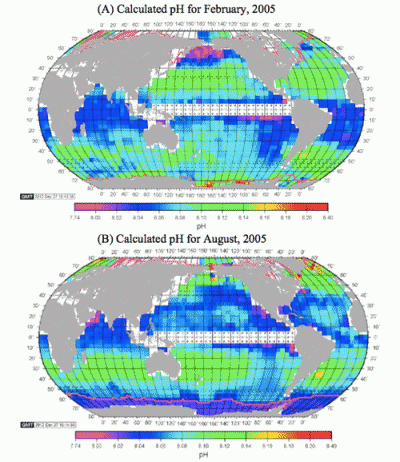
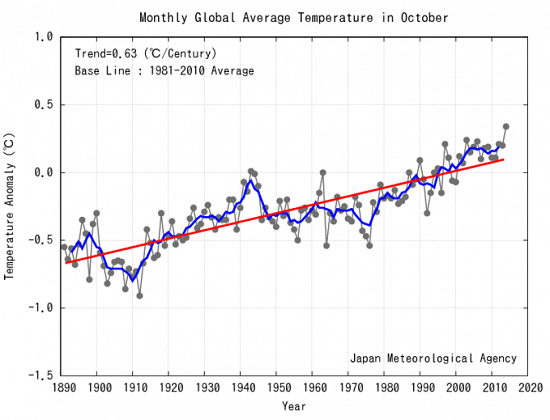
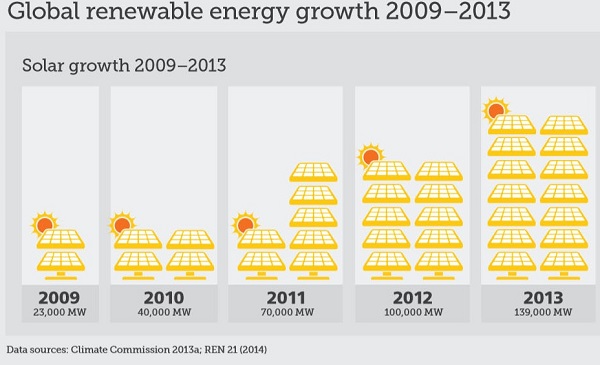
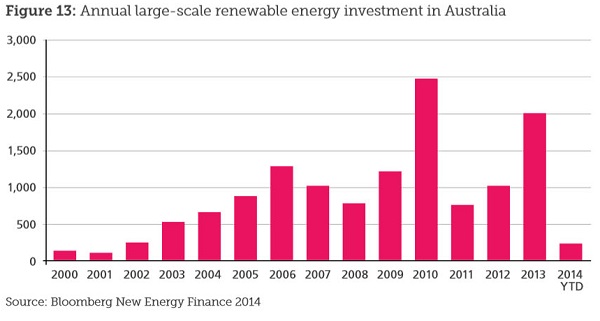
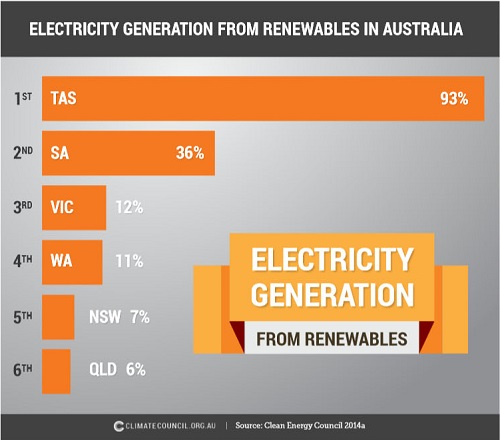
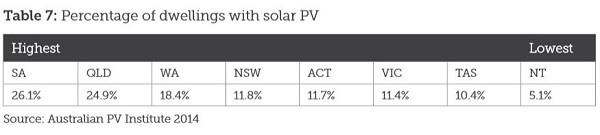
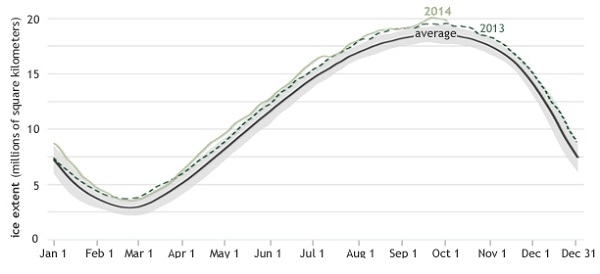
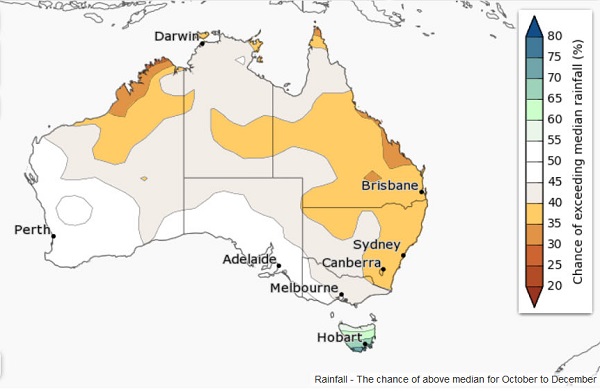
1. Hot and cold
My sister in Toronto tells us how cold it has been. She can’t remember the last time it reached -5°C.
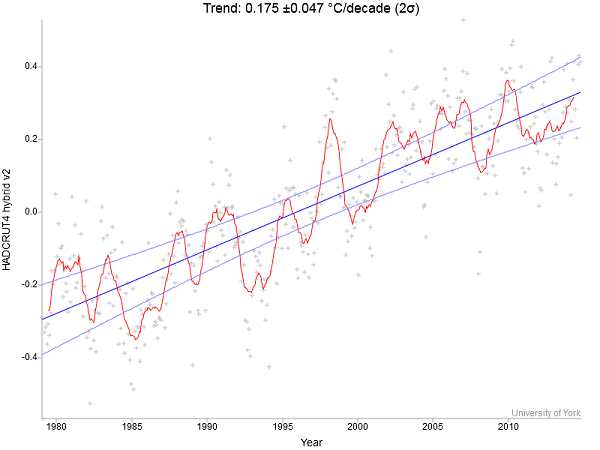
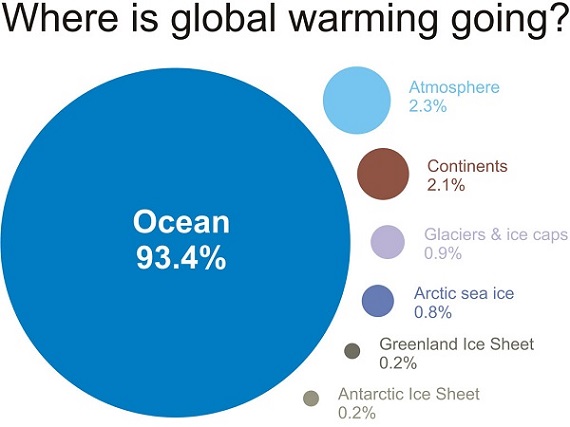
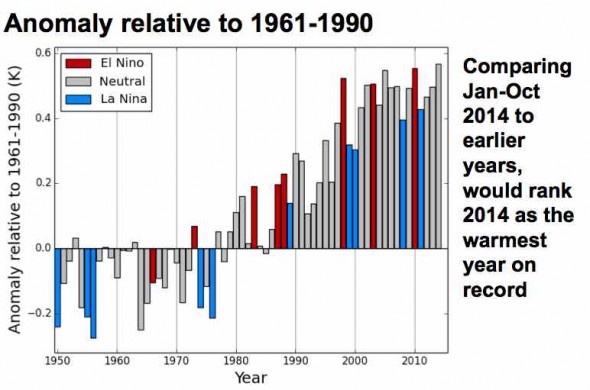
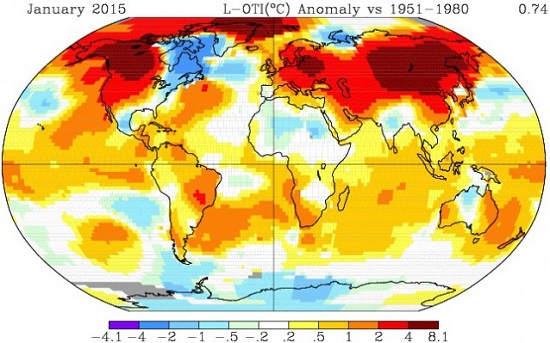
Yet NASA finds that Feb 2014 to Jan 2015 was the hottest 12 months on record. The picture tells the story:
2. Record megadroughts predicted
The American Southwest and the great Plains could experience the worst megadroughts in ancient and modern times.
According to the findings, future droughts in both regions will be more severe than even the hottest, driest megadroughts of the 12th and 13th centuries, which are believed to have contributed to the fall of ancient Native American civilizations that inhabited the Southwest, such as the Pueblo Indians.
Climate Central gives the odds.
The chances of a megadrought (lasting 35 years or longer) are up to 50%.
The odds of a decade-long drought are around 90%.
There’s also a 5-10 percent chance that parts of the region could see a state of “permanent” megadrought lasting 50 years or longer under the highest-warming scenario, a greenhouse gas emissions path we’re currently on.
3. New era of climate action and hope
Christiana Figueres reckons 2015 is going to be a transformational year in climate change action. She of course is the boss-person of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) which is sponsoring the Paris talks in December.
Amongst other things she mentions the June Live Earth concerts initiated by Al Gore and Kevin Wall (reviving their 2007 effort) to be held in New York, South Africa, Australia, China, Brazil and Paris.
She also plugs the UNFCCC’s Momentum for Change initiative, including Lighthouse Activities.
4. UK parties in pact on climate change
David Cameron, Nick Clegg and Ed Miliband have agreed to work together to tackle climate change, as they warned it posed a threat to national security and economic prosperity.
In what might be seen as a surprising move in the run-up to the general election, the three party leaders have pledged to work “across party lines” to agree cuts to the UK’s carbon emissions.
They have also signed up to seeking a “fair, strong, legally binding” international climate deal, set to be negotiated in Paris at the end of the year, to limit global temperature rises to below 2C – the level beyond which “dangerous” climate change is expected.
And they pledged to move to a low-carbon economy, ending the use of coal without technology to capture and store its emissions for power generation. (Emphasis added)
Tesla will start production in about six months, all going well.
“We are going to unveil the Tesla home battery, the consumer battery that would be for use in people’s houses or businesses fairly soon.”
“Some will be like the Model S pack: something flat, 5 inches off the wall, wall mounted, with a beautiful cover, an integrated bi-directional inverter, and plug and play.”
Thanks to Geoff Henderson who linked to this one recently at Saturday Salon. Yes, it could indeed be a game changer.
6. Laser ignition to replace spark plugs
A team at Princeton Optronics working on replacing conventional spark plugs with laser igniters has produced a running engine and they claim that replacing spark ignition with lasers could improve the efficiency of gasoline powered engines by 27%. Considering that the basic design of the spark plug hasn’t really changed in over a century, this would be a revolutionary step, frickin’ lasers or not.
Because the spark plug is located on the edge of the combustion chamber, not all of the fuel is combusted. Laser ignition can be directed to the centre of the chamber, or in fact to multiple parts of the chamber in extremely rapid succession. Ignition can also be more accurately timed in relation to the movement of the piston. The result is a more complete burn and greater fuel efficiency.
7. Climate oscillations and the global warming faux pause
Michael Mann posts on research he was conducted, with others, on multidecadal climate oscillations in the Pacific and the Atlantic Oceans. They found that the Pacific dominates and was the predominant cause of a slight slowing in predicted warming over the past decade-and-a-half or so.
It is possible that the downturn in the PMO [Pacific Multidecadal Oscillation] itself reflects a “dynamical response” of the climate to global warming. Indeed, I have suggested this possibility before. But the state-of-the-art climate model simulations analyzed in our current study suggest that this phenomenon is a manifestation of purely random, internal oscillations in the climate system.
This has implications for the future.
Given the pattern of past historical variation, this trend will likely reverse with internal variability, instead adding to anthropogenic warming in the coming decades.
The “false pause” may simply have been a cause for false complacency, when it comes to averting dangerous climate change.
Reminder Climate clippings is an open thread and can be used for exchanging news and views on climate.