This post was written in October 2012 trialling the site. I’ve decided to leave it in time sequence and fiddle the numbering.
1. Did climate change shape human evolution?
There’s no evidence yet that it did according to Richard Leakey.
I’m not sure about his four key questions, though. Yes, bipedalism seems to be important as does using tools to make tools. But I can’t see the importance of migration out of Africa as important to our evolution. Apart from picking up some Neanderthal genes presumably in a palm grove somewhere in the Middle East, which did boost our immune system, those of us who left Africa are much the same genetically as those who stayed behind.
I’d say the development of language was important. If you want a fourth I’d suggest our patterns of social organisation – how we interact and how we co-operate within groups. But I don’t know how much of that is in our genes.
2. Aid for climate refugees
Speaking of climate and migration, displacement by extreme weather events does not qualify you as a refugee under present UN arrangements. The International Organisation of Migration (IOM) hopes this will change at the annual United Nations climate change summit to be held in Qatar later this year, gaining access to the Green Climate Fund (GCF) and other sources. It seems that 42 million people were displaced by storms, floods and droughts in Asia and the Pacific during 2010 and 2011.
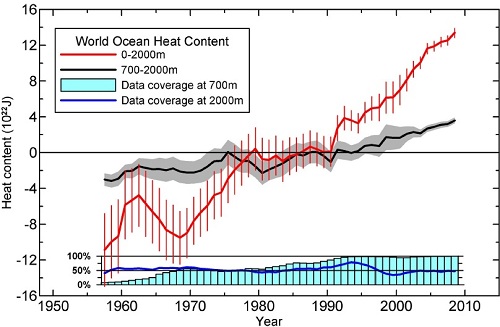
3. Ocean heat content update
Skeptical Science recently posted on an update by Levitus et al on ocean heat content, which increases apace. Around 93% of additional warming goes into the ocean which is truly vast with, for example, an average depth of around 3,790 metres. This graph indicates the changing heat content within bands of the upper 2000m:
4. Southern Ocean research shows decrease in dense Antarctic bottom water

Antarctic Bottom Water is a massive current of super dense salty water which used to be which used to occupy the bottom mile of the Great Southern Ocean. Used to. Researchers are now able to report that the current is diminished by 60% compared to what it was in 1970.
Antarctic Bottom Water is colder than the normal freezing point and is a vast store of CO2. Understanding changes in this deep ocean current are crucial to understanding the likely future of global climate patterns as the planet warms. The researchers have not only been able to make direct observations, they have distributed buoys which should be able to provide data at times of the year when field work is impossible.
5. Plants flower faster than climate change models predict
For years scientists have been doing experiments to find out how much earlier plants will flower and leaf with global warming. A new study using field observations has found that plants are responding much faster than they had thought. Their research suggests that that spring flowering and leafing will continue to advance at the rate of 5 to 6 days per year for every degree celsius of warming.
What surprises me is that they thought they could model natural conditions in the lab.
It seems they will have to rethink the impacts of global warming on ecosystems and food production.
See also Science Daily.
6. Climate change experimentation goes bush
Another approach is to manipulate the environment on a large scale and monitor what happens. Researchers are using to control the amount of CO2 available to plants.
The idea is explore the role of “Australia’s large tracts of undeveloped land, known as bush” in storing carbon. They will be able to add carbon or take it away.
I’m not sure it doesn’t suffer from the same problems as experiments with plants, where only one variable was controlled, neglecting changes in precipitation patterns and cloudiness, for example.
7. Wind farms do not cause global warming
There has been a raft of articles in the MSM suggesting that wind farms cause global warming, mainly in the headlines, it seems.
In fact a study of some large wind farms in remote areas of Texas found local warming. The authors don’t know what’s going on but the suggestion is that thermal energy is being redistributed, perhaps by pulling down warmer air from higher altitudes during the nights.
For the spinning blades of wind turbines to increase the overall temperature of the planet some basic laws of physics would need to be rewritten.